PINNs: grad-div system 2D¶
Solves a grad-div system in 2D with Dirichlet boundary conditions using a PINN.
\[\begin{split}\left\{\begin{array}{rl} -\nabla (\nabla \cdot u) + u & = f \text{ in } \Omega \times M \\
u & = g \text{ on } \partial \Omega \times M\end{array}\right.\end{split}\]
where \(u: \Omega \times M \to \mathbb{R}^2\) is the unknown function, \(\Omega \subset \mathbb{R}^2\) is the spatial domain and \(M \subset \mathbb{R}\) is the parametric domain and \(f: \Omega \times M \to \mathbb{R}^2\).
The equation is solved on a square domain with PINNs with energy natural gradient preconditioning and PINNs with Anagram preconditioning.
Weak and strong boundary conditions are used.
[1]:
from typing import Callable, Tuple
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
from scimba_torch.approximation_space.abstract_space import AbstractApproxSpace
from scimba_torch.approximation_space.nn_space import NNxSpace
from scimba_torch.domain.meshless_domain.domain_2d import Square2D
from scimba_torch.integration.monte_carlo import DomainSampler, TensorizedSampler
from scimba_torch.integration.monte_carlo_parameters import UniformParametricSampler
from scimba_torch.neural_nets.coordinates_based_nets.mlp import GenericMLP
from scimba_torch.numerical_solvers.elliptic_pde.pinns import (
AnagramPinnsElliptic,
NaturalGradientPinnsElliptic,
)
from scimba_torch.plots.plots_nd import plot_abstract_approx_spaces
from scimba_torch.utils.scimba_tensors import LabelTensor, MultiLabelTensor
from scimba_torch.utils.typing_protocols import VarArgCallable
torch.manual_seed(0)
class GradDiv2D:
def __init__(
self,
space: AbstractApproxSpace,
f: Callable,
g: Callable,
**kwargs,
):
self.space = space
self.f = f
self.g = g
self.linear = True
self.residual_size = 2
self.bc_residual_size = 2
def grad(
self,
w: torch.Tensor | MultiLabelTensor,
y: torch.Tensor | LabelTensor,
) -> torch.Tensor | Tuple[torch.Tensor, ...]:
return self.space.grad(w, y)
def rhs(
self, w: MultiLabelTensor, x: LabelTensor, mu: LabelTensor
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor]:
return self.f(x, mu)
def bc_rhs(
self, w: MultiLabelTensor, x: LabelTensor, n: LabelTensor, mu: LabelTensor
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor]:
return self.g(x, mu)
def operator(
self, w: MultiLabelTensor, xs: LabelTensor, mu: LabelTensor
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor]:
x, y = xs.get_components()
u, v = w.get_components()
u_x, u_y = self.grad(u, xs)
u_xx, u_xy = self.grad(u_x, xs)
v_x, v_y = self.grad(v, xs)
v_yx, v_yy = self.grad(v_y, xs)
return u_xx + v_yx + u, u_xy + v_yy + v
def restrict_to_component(self, i: int, func):
return lambda *args: func(*args)[i : i + 1, ...]
def functional_operator(
self,
func: VarArgCallable,
x: torch.Tensor,
mu: torch.Tensor,
theta: torch.Tensor,
) -> torch.Tensor:
uv_x = func(x, mu, theta)
grad_u = self.restrict_to_component(0, torch.func.jacrev(func, 0))
grad_v = self.restrict_to_component(1, torch.func.jacrev(func, 0))
hessian_u = torch.func.jacrev(grad_u, 0)(x, mu, theta).squeeze()
hessian_v = torch.func.jacrev(grad_v, 0)(x, mu, theta).squeeze()
res = hessian_u[..., 0] + hessian_v[..., 1] + uv_x
return res
# Dirichlet conditions
def bc_operator(
self, w: MultiLabelTensor, x: LabelTensor, n: LabelTensor, mu: LabelTensor
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor]:
u, v = w.get_components()
return u, v
def functional_operator_bc(
self,
func: VarArgCallable,
x: torch.Tensor,
n: torch.Tensor,
mu: torch.Tensor,
theta: torch.Tensor,
) -> torch.Tensor:
return func(x, mu, theta)
def exact_solution(xs: LabelTensor, mu: LabelTensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x, y = xs.get_components()
alpha = mu.get_components()
return torch.cat(
(
torch.sin(2.0 * torch.pi * x) * torch.sin(2.0 * torch.pi * y),
alpha * torch.sin(2.0 * torch.pi * x) * torch.sin(2.0 * torch.pi * y),
),
dim=-1,
)
def f_rhs(xs: LabelTensor, mu: LabelTensor) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor]:
x, y = xs.get_components()
alpha = mu.get_components()
PI = torch.pi
cos_x = torch.cos(2.0 * PI * x)
cos_y = torch.cos(2.0 * PI * y)
sin_x = torch.sin(2.0 * PI * x)
sin_y = torch.sin(2.0 * PI * y)
f1 = (1 - 4 * PI**2) * sin_x * sin_y + 4 * PI**2 * alpha * cos_x * cos_y
f2 = (1 - 4 * PI**2 * alpha) * sin_x * sin_y + 4 * PI**2 * cos_x * cos_y
return f1, f2
def f_bc(xs: LabelTensor, mu: LabelTensor) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor]:
x, _ = xs.get_components()
return torch.zeros_like(x), torch.zeros_like(x)
bc_weight = 10.0
domain_mu = [(0.75, 0.75)]
domain_x = Square2D([(0.0, 1), (0.0, 1)], is_main_domain=True)
sampler = TensorizedSampler(
[DomainSampler(domain_x), UniformParametricSampler(domain_mu)]
)
ENG preconditioned PINN, weak boundary conditions¶
[2]:
space = NNxSpace(2, 1, GenericMLP, domain_x, sampler, layer_sizes=[64])
pde = GradDiv2D(space, f_rhs, f_bc)
pinns = NaturalGradientPinnsElliptic(
pde,
bc_type="weak",
bc_weight=bc_weight,
one_loss_by_equation=True,
matrix_regularization=1e-6,
)
pinns.solve(epochs=100, n_collocation=3000, n_bc_collocation=1000, verbose=False)
Training: 100%|||||||||||||||||| 100/100[00:08<00:00] , loss: 1.2e+03 -> 8.9e-04
Anagram preconditioned PINN, weak boundary conditions¶
[3]:
space2 = NNxSpace(2, 1, GenericMLP, domain_x, sampler, layer_sizes=[64])
pde2 = GradDiv2D(space2, f_rhs, f_bc)
pinns2 = AnagramPinnsElliptic(
pde2,
bc_type="weak",
bc_weight=bc_weight,
one_loss_by_equation=True,
svd_threshold=5e-2,
)
pinns2.solve(epochs=100, n_collocation=3000, n_bc_collocation=1000, verbose=False)
Training: 100%|||||||||||||||||| 100/100[00:16<00:00] , loss: 1.2e+03 -> 5.5e-03
[4]:
plot_abstract_approx_spaces(
pinns.space,
domain_x,
domain_mu,
loss=pinns.losses,
error=exact_solution,
draw_contours=True,
n_drawn_contours=20,
title="solving GradDiv2D with ENG preconditioned PINN",
)
plt.show()
plot_abstract_approx_spaces(
pinns2.space,
domain_x,
domain_mu,
loss=pinns2.losses,
error=exact_solution,
draw_contours=True,
n_drawn_contours=20,
title="solving GradDiv2D with Anagram preconditioned PINN",
)
plt.show()
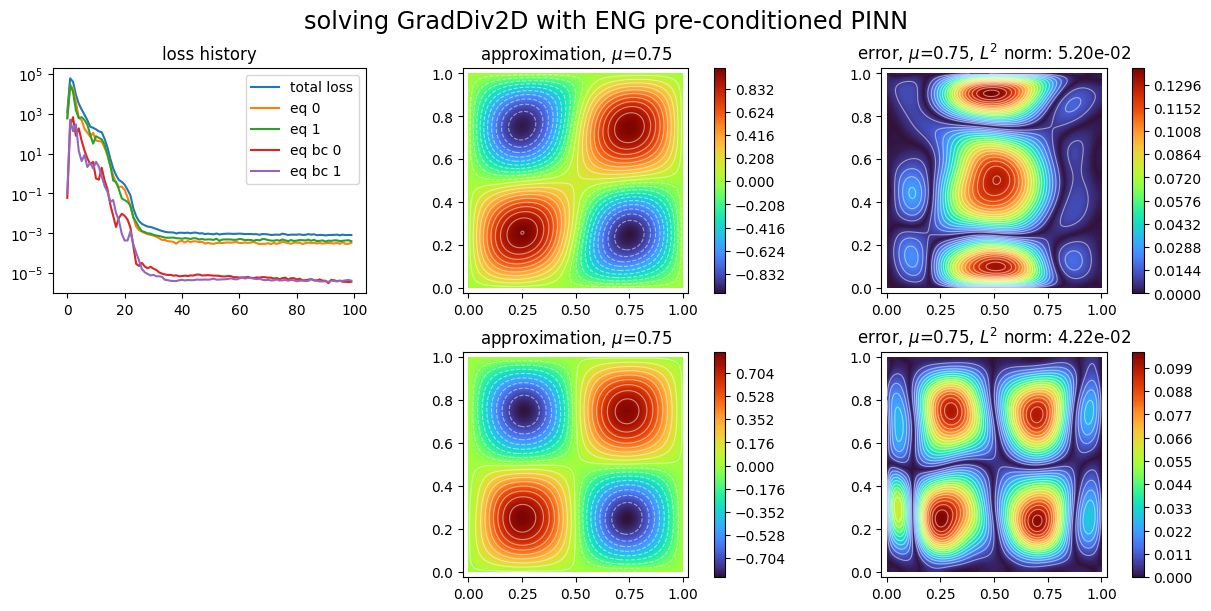
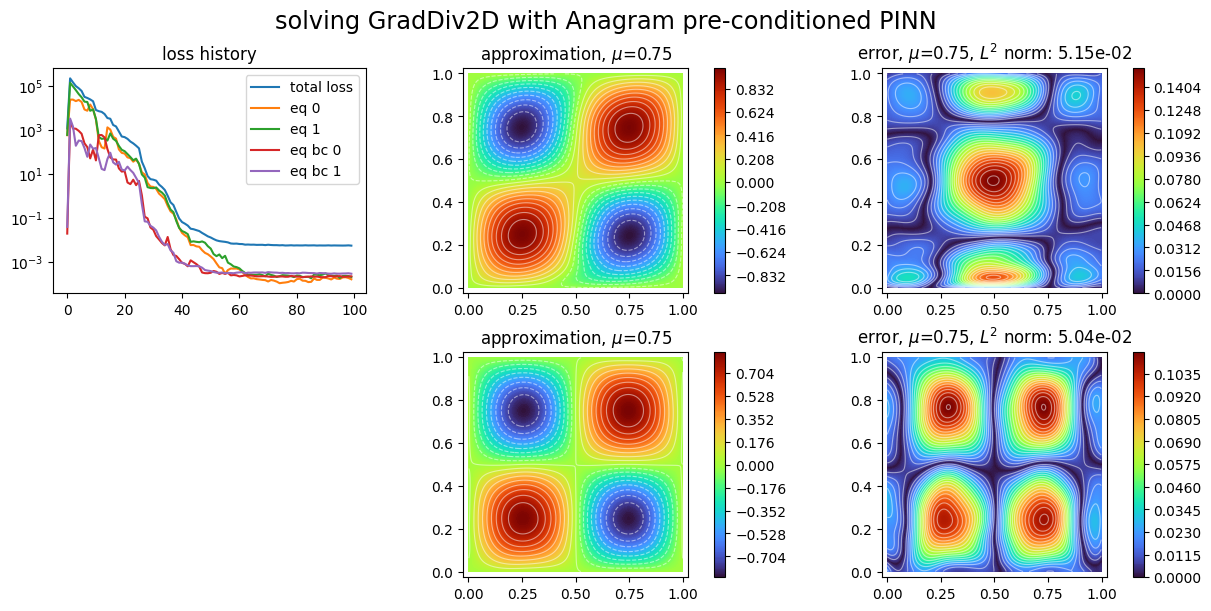
Strong boundary conditions¶
[5]:
def post_processing(inputs: torch.Tensor, xs: LabelTensor, mu: LabelTensor):
x, y = xs.get_components()
# _ = mu.get_components()
phi = x * (x - 1.0) * y * (y - 1.0)
return inputs * phi
def functional_post_processing(
func, x: torch.Tensor, mu: torch.Tensor, theta: torch.Tensor
) -> torch.Tensor:
phi = x[0] * (x[0] - 1.0) * x[1] * (x[1] - 1.0)
return func(x, mu, theta) * phi
ENG preconditioned PINN, strong boundary conditions¶
[6]:
space3 = NNxSpace(2, 1, GenericMLP, domain_x, sampler, layer_sizes=[64], post_processing=post_processing)
pde3 = GradDiv2D(space3, f_rhs, f_bc)
pinns3 = NaturalGradientPinnsElliptic(
pde3,
bc_type="strong",
one_loss_by_equation=True,
matrix_regularization=1e-6,
functional_post_processing=functional_post_processing,
)
pinns3.solve(epochs=50, n_collocation=3000, verbose=False)
Training: 100%|||||||||||||||||||| 50/50[00:05<00:00] , loss: 1.2e+03 -> 2.0e-03
Anagram preconditioned PINN, strong boundary conditions¶
[7]:
space4 = NNxSpace(2, 1, GenericMLP, domain_x, sampler, layer_sizes=[64], post_processing=post_processing)
pde4 = GradDiv2D(space4, f_rhs, f_bc)
pinns4 = AnagramPinnsElliptic(
pde4,
bc_type="strong",
one_loss_by_equation=True,
svd_threshold=5e-3,
functional_post_processing=functional_post_processing,
)
pinns4.solve(epochs=200, n_collocation=3000, verbose=False)
Training: 100%|||||||||||||||||| 200/200[00:36<00:00] , loss: 1.2e+03 -> 2.7e-03
[8]:
plot_abstract_approx_spaces(
pinns3.space,
domain_x,
domain_mu,
loss=pinns3.losses,
error=exact_solution,
draw_contours=True,
n_drawn_contours=20,
title="solving GradDiv2D with ENG preconditioned PINN",
)
plt.show()
plot_abstract_approx_spaces(
pinns4.space,
domain_x,
domain_mu,
loss=pinns4.losses,
error=exact_solution,
draw_contours=True,
n_drawn_contours=20,
title="solving GradDiv2D with Anagram preconditioned PINN",
)
plt.show()
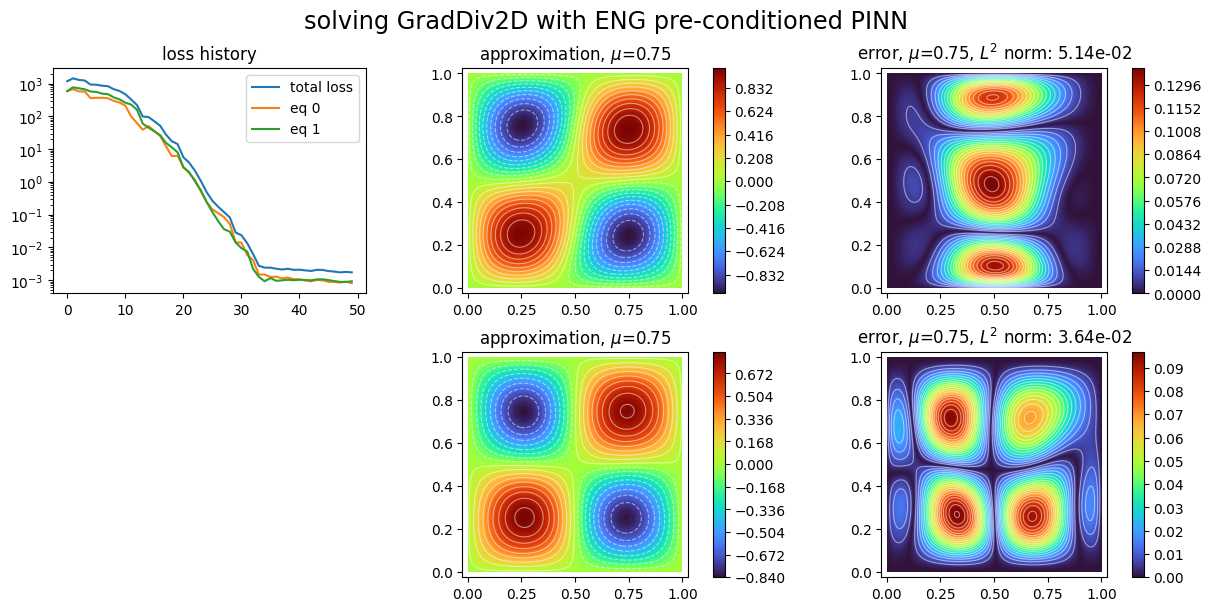
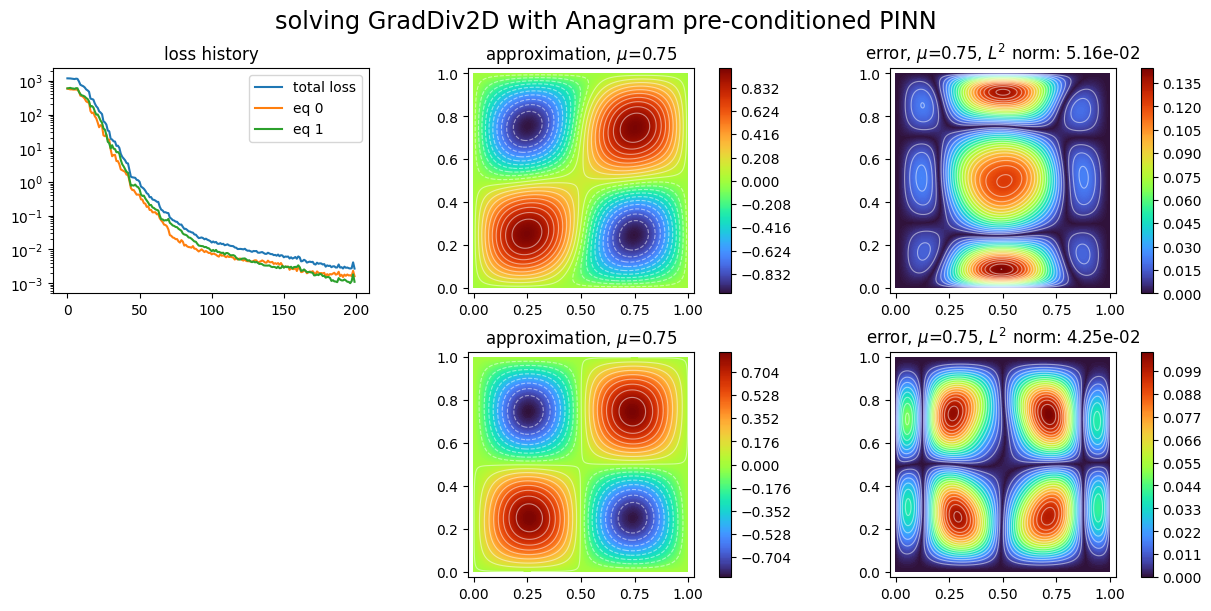
[ ]: