Time discrete: rotating transport¶
Solves a rotating transport equation:
\[\begin{split}\left\{\begin{array}{lll}
\partial_t u + a({\bf x}) \cdot \nabla u &= 0, & {\bf x}\in\Omega, t\in (0,1)\\
u(0,{\bf x},\mu) &= u_0({\bf x},\mu), & {\bf x}\in\Omega \\
u(t,{\bf x},\mu) &= 0, & {\bf x}\in\partial\Omega, t\in (0,1)
\end{array}\right.\end{split}\]
where: \(\mu = (v,c)\), \({\bf x} = (x, y)\), \(\Omega\) is the unit disk and
\[\begin{split}a({\bf x}) := \left( \begin{array}{c} 2\pi y \\ -2\pi x \end{array}\right),\end{split}\]
with initial condition
\[u_0({\bf x},\mu) := u_{ex}(0,{\bf x},\mu)\]
where
\[u_{ex}(t,{\bf x},\mu) := 1 + \text{exp}\left(
-\dfrac{1}{v^2} \left(
\left( x - c \cos(2\pi t)\right)^2
+ \left( y - c \sin(2\pi t)\right)^2
\right)
\right).\]
is the exact solution of the considered problem.
The equation is solved using the neural Galerkin scheme with a natural gradient projector; weak initial and boundary conditions are used.
[1]:
from typing import Callable
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scimba_torch.approximation_space.abstract_space import AbstractApproxSpace
from scimba_torch.approximation_space.nn_space import NNxSpace
from scimba_torch.domain.meshless_domain.domain_2d import Disk2D
from scimba_torch.integration.monte_carlo import DomainSampler, TensorizedSampler
from scimba_torch.integration.monte_carlo_parameters import UniformParametricSampler
from scimba_torch.neural_nets.coordinates_based_nets.mlp import GenericMLP
from scimba_torch.numerical_solvers.temporal_pde.neural_galerkin import NeuralGalerkin
from scimba_torch.numerical_solvers.temporal_pde.time_discrete import (
TimeDiscreteNaturalGradientProjector,
)
from scimba_torch.physical_models.temporal_pde.abstract_temporal_pde import TemporalPDE
from scimba_torch.plots.plot_time_discrete_scheme import plot_time_discrete_scheme
from scimba_torch.utils.scimba_tensors import LabelTensor, MultiLabelTensor
class RotatingTransport(TemporalPDE):
def __init__(self, space: AbstractApproxSpace, a: Callable, f_ic: Callable):
self.space = space
self.a = a
self.f_ic = f_ic
def grad(self, w: torch.Tensor, z: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
# returns the gradient of w with respect to z
return self.space.grad(w, z)
# the right hand side of the equation; w is the evaluation of the approximation at
# t, x, y, mu
def rhs(
self, w: MultiLabelTensor, t: LabelTensor, xy: LabelTensor, mu: LabelTensor
) -> torch.Tensor:
x, _ = xy.get_components()
return 0 * x
def bc_rhs( # the left hand side of the boundary conditions
self,
w: MultiLabelTensor,
t: LabelTensor,
xy: LabelTensor,
n: LabelTensor,
mu: LabelTensor,
) -> torch.Tensor:
x, _ = xy.get_components()
return 0 * x
def initial_condition( # the left hand side of the initial conditions
self, xy: LabelTensor, mu: LabelTensor
) -> torch.Tensor:
return self.f_ic(xy, mu)
def time_operator( # the time dependant part of the left hand side of the equation
self, w: MultiLabelTensor, t: LabelTensor, xy: LabelTensor, mu: LabelTensor
) -> torch.Tensor:
return self.grad(w, t)
# the space dependant part of the left hand side of the equation
def space_operator(
self, w: MultiLabelTensor, t: LabelTensor, xy: LabelTensor, mu: LabelTensor
) -> torch.Tensor:
grad_u = torch.cat(list(self.grad(w.get_components(), xy)), dim=1)
return torch.einsum("bi,bi-> b", self.a(t, xy, mu), grad_u)[..., None]
def operator( # already defined in TemporalPDE; given here for completeness
self, w: MultiLabelTensor, t: LabelTensor, xy: LabelTensor, mu: LabelTensor
) -> torch.Tensor:
return self.space_operator(w, t, xy, mu) + self.time_operator(w, t, xy, mu)
# Dirichlet condition: u(t, x, mu) = 0
def bc_operator( # the left hand side of the equation
self,
w: MultiLabelTensor,
t: LabelTensor,
x: LabelTensor,
n: LabelTensor,
mu: LabelTensor,
) -> torch.Tensor:
return w.get_components()
def exact_solution(t: LabelTensor, xy: LabelTensor, mu: LabelTensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x, y = xy.get_components()
t_ = t.get_components()
c, v = mu.get_components()
x_t = torch.cos(2 * torch.pi * t_)
y_t = torch.sin(2 * torch.pi * t_)
return 1 + torch.exp(-0.5 / v**2 * ((x - c * x_t) ** 2 + (y - c * y_t) ** 2))
def initial_condition(xy: LabelTensor, mu: LabelTensor) -> torch.Tensor:
t = LabelTensor(torch.zeros((xy.shape[0], 1)))
return exact_solution(t, xy, mu)
def a(t: LabelTensor, xy: LabelTensor, mu: LabelTensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x, y = xy.get_components()
return torch.cat((-2 * torch.pi * y, 2 * torch.pi * x), dim=1)
torch.random.manual_seed(0)
domain_x = Disk2D((0.0, 0.0), 1.0, is_main_domain=True)
domain_mu = [[0.3, 0.3], [0.1, 0.1]]
sampler = TensorizedSampler(
[
DomainSampler(domain_x),
UniformParametricSampler(domain_mu),
]
)
space = NNxSpace(1, 2, GenericMLP, domain_x, sampler, layer_sizes=[8, 16, 8])
pde = RotatingTransport(space, a, initial_condition)
projector = TimeDiscreteNaturalGradientProjector(pde)
scheme = NeuralGalerkin(pde, projector, scheme="rk4")
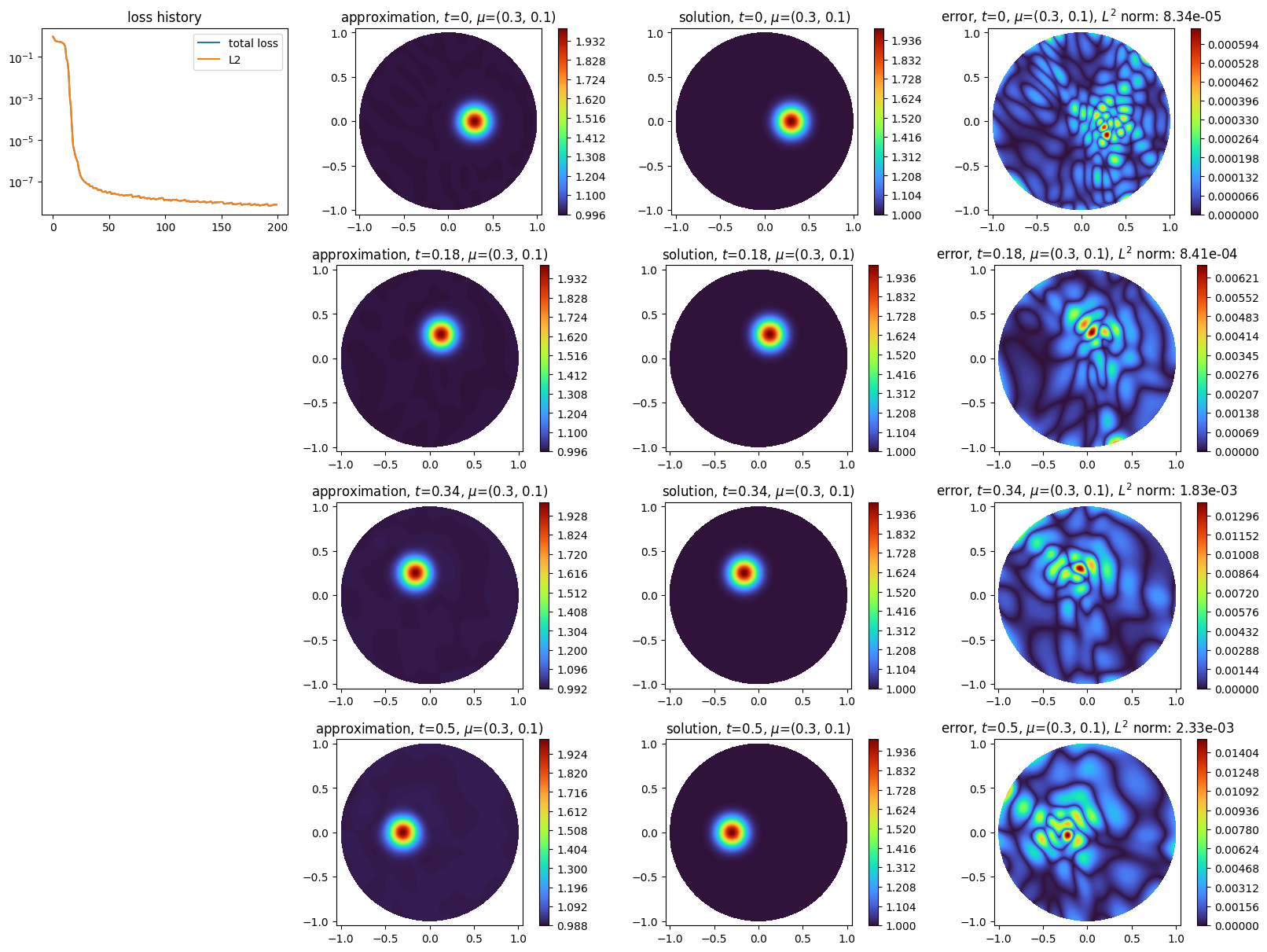
scheme.initialization(epochs=200, n_collocation=15_000, verbose=False)
scheme.solve(dt=0.02, final_time=0.5, verbose=False, nb_keep=2)
plot_time_discrete_scheme(
scheme,
solution=exact_solution,
error=exact_solution,
)
plt.show()
Initialization: 100%|||||||||||| 200/200[00:05<00:00] , loss: 9.5e-01 -> 6.7e-09
Time loop: 100%|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||| 0.5/0.5 [00:00<00:00]
[ ]: