Learning the Signed Distance Function of a shape¶
An example illustrating rsdf nn to learn a bean shape from a file of points.
[1]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
from scimba_torch.geometry.parametric_hypersurface import (
ParametricHyperSurface,
)
from scimba_torch.geometry.regularized_sdf_projectors import (
learn_regularized_sdf,
)
from scimba_torch.geometry.utils import write_points_normals_to_file
from scimba_torch.integration.monte_carlo import DomainSampler, TensorizedSampler
from scimba_torch.integration.monte_carlo_parameters import UniformParametricSampler
from scimba_torch.optimizers.optimizers_data import OptimizerData
from scimba_torch.plots.plot_regularized_sdf_projector import (
plot_regularized_sdf_projector,
)
from scimba_torch.utils import Mapping
torch.manual_seed(0)
# define the bean 2d function
def bean_2d_function(t: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""The bean 2d function.
Args:
t: The argument.
Returns:
c(t).
"""
a, b = 3, 5
sin = torch.sin(t)
cos = torch.cos(t)
x = (sin**a + cos**b) * cos
y = (sin**a + cos**b) * sin
return torch.cat((x, y), dim=-1)
def generate_bean_filepoints(n: int, filename: str) -> None:
# create the bean mapping, compose it with a rotation
bean_2d_mapping = Mapping(1, 2, bean_2d_function)
bean_2d_mapping = Mapping.compose(bean_2d_mapping, Mapping.rot_2d(-torch.pi / 2))
# create a parametric hypersurface
bean_2d = ParametricHyperSurface([(0.0, 2 * torch.pi)], bean_2d_mapping)
# generate a tuple of n points, n normals
points, normals = bean_2d.sample(n)
# write the samples to the file
write_points_normals_to_file(points, normals, filename)
filename = "bean.xy"
generate_bean_filepoints(2000, filename)
ginn = learn_regularized_sdf(
points_file=filename,
mode="new",
epochs=200,
n_collocation=4000,
n_bc_collocation=2000,
verbose=False,
)
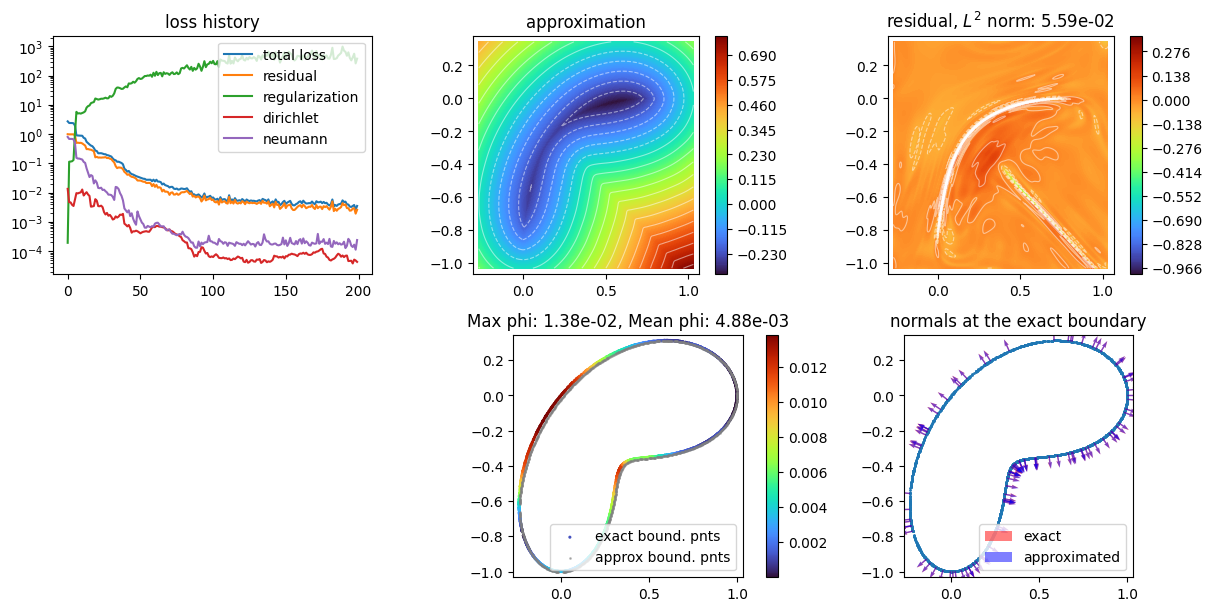
# plot the result
plot_regularized_sdf_projector(
ginn,
n_visu=512,
draw_contours=True,
n_drawn_contours=20,
)
plt.show()
Training: 100%|||||||||||||||||| 200/200[00:26<00:00] , loss: 2.7e+00 -> 2.6e-03