ScimBa¶
Scimba is a Python library that implements varying Scientific Machine Learning (SciML) methods for PDE problems, as well as tools for hybrid numerical methods.
The current version of the code solves parametric PDEs using various nonlinear approximation spaces such as neural networks, low-rank approximations, and nonlinear kernel methods. These methods:
can handle complex geometries generated via level-set techniques and mappings, including sub-volumetric and surface domains;
support function projections as well as elliptic, time-dependent, and kinetic parametric PDEs;
are compatible with both space–time algorithms (PINN, Deep Ritz) and time-sequential ones (discrete PINNs, neural Galerkin and neural semi-Lagrangian schemes).
To achieve this, the code provides several optimization strategies, including:
Adam, L-BFGS, SS-BFGS and SS-Broyden;
natural gradient methods (for neural network-based models);
hybrid least-squares approaches.
The current version of Scimba relies on a PyTorch backend. A JAX version is under development.
Documentation: https://www.scimba.org/
Code repository: https://gitlab.com/scimba/scimba/
Install¶
uv is the preferred tool to install scimba, but you can
also use pip.
In any case, it is strongly recommended to isolate your installation in a virtual
environment (uv does this for you).
If your project is handled by a pyproject.toml:
uv init
uv add scimba
otherwise:
uv pip install scimba
pip install scimba
Note
If you are using an AMD GPU, you need to set the appropriate index URL to install the PyTorch ROCm version prior to installing scimba.
export UV_EXTRA_INDEX_URL="https://download.pytorch.org/whl/rocm6.4"
export PIP_INDEX_URL="https://download.pytorch.org/whl/rocm6.4"
Learning ScimBa¶
If you are new to Physics Informed Neural Networks, a good start may be to follow this course: https://rimbach.gitlabpages.inria.fr/fabrique-ton-pinns.
In the meantime, here is a gallery of tutorials and examples to get you started with ScimBa.
Tutorials¶
Each tutorial is a single Jupyter notebook that helps you get started with Scimba.
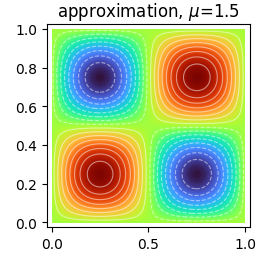
Solve 2D Laplacian problems with Dirichlet boundary conditions.
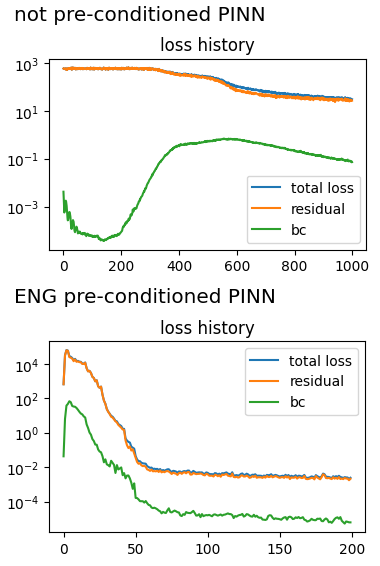
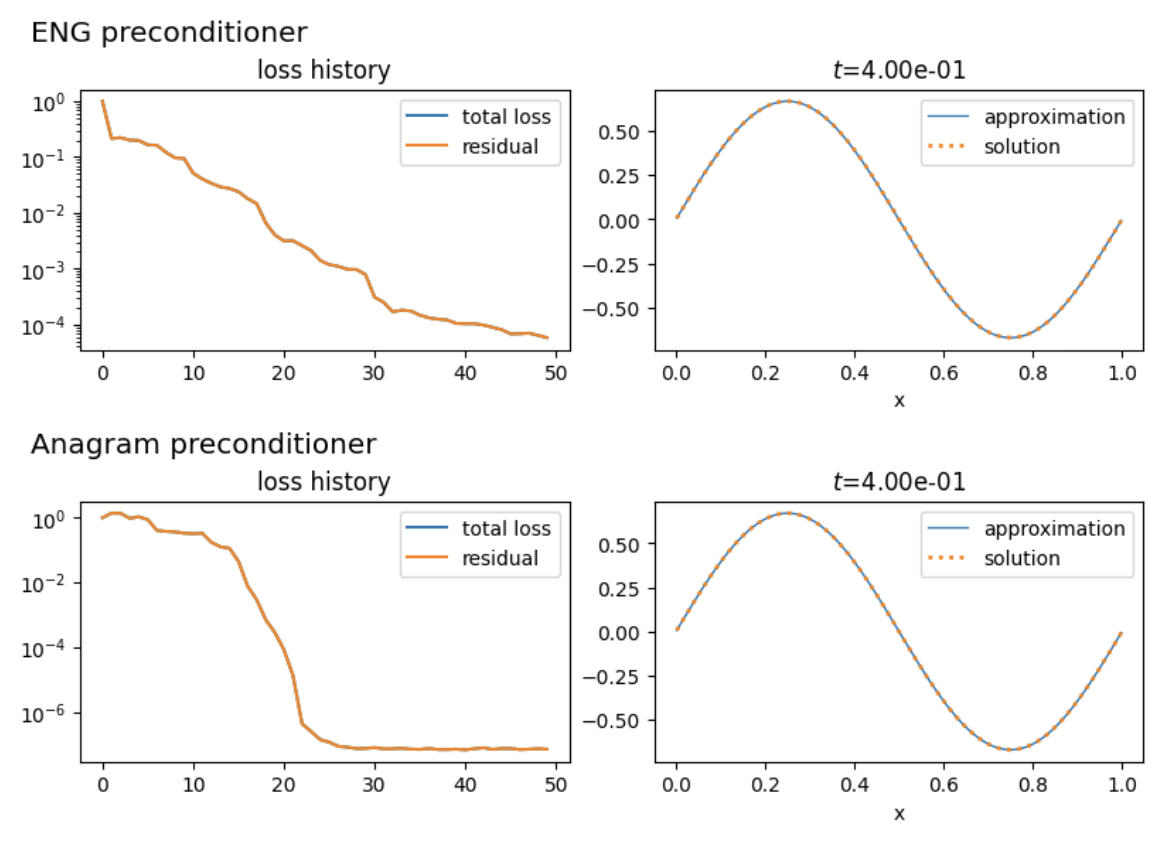
Setup an equation for applying preconditioners.
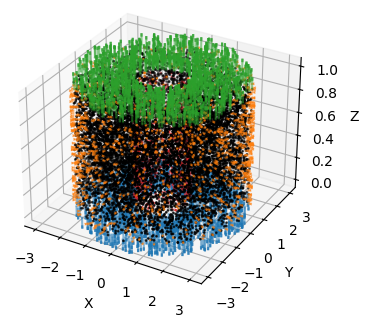
Learn how to define and work with computational domains.
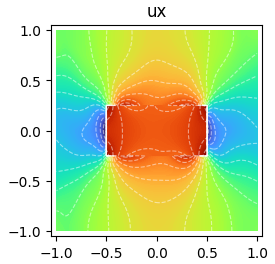
Learn how to define physical models and PDEs in Scimba for different problem types.
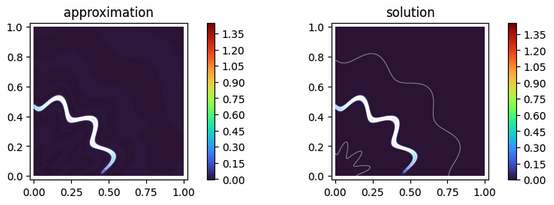
Learn how to approximate a function given as an evaluation procedure with a network based approximation space.

Save and load PINNs.
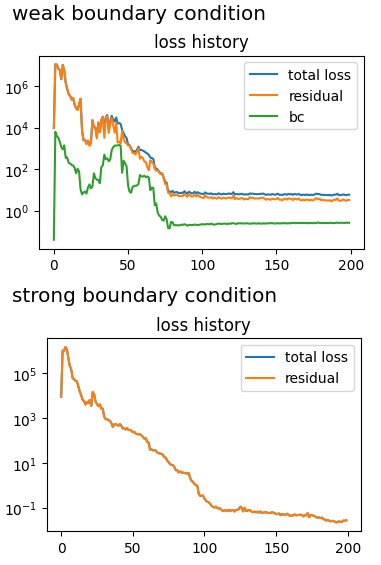
Implementation of strong boundary conditions in 2D problems.
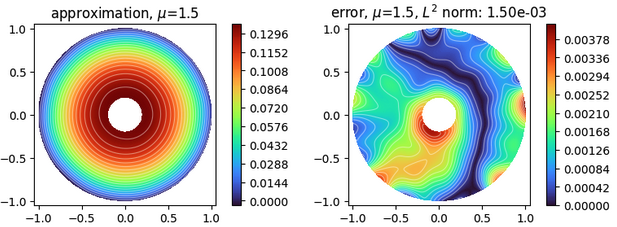
Handling mixed boundary conditions.
Explore time discretization methods for temporal PDEs.
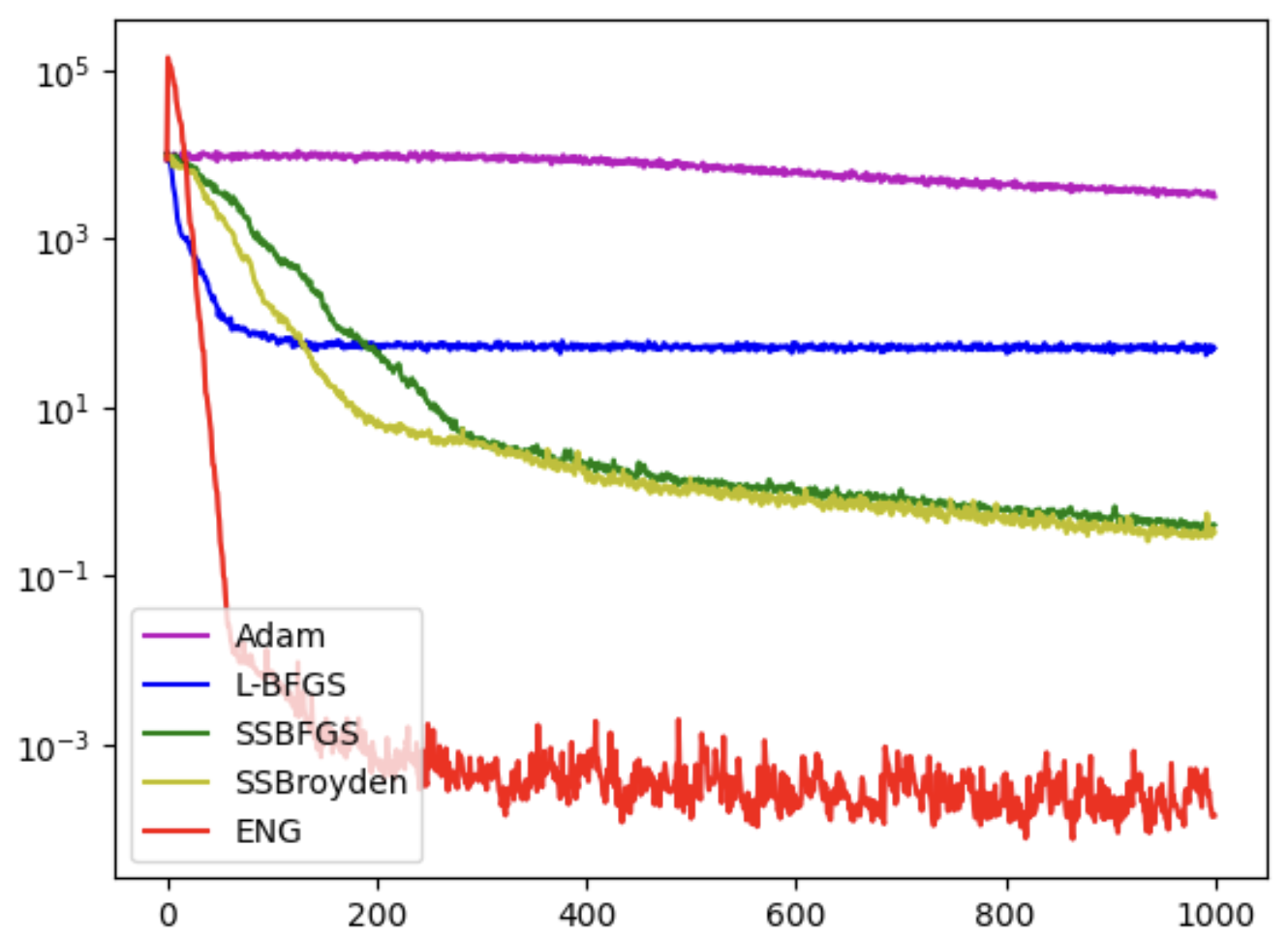
Scimba optimizers how to.
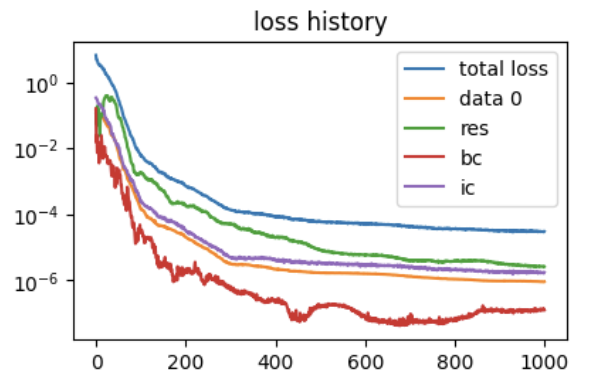
How to define and tune losses and losses weights.
Examples¶
Each example is a single Jupyter notebook.
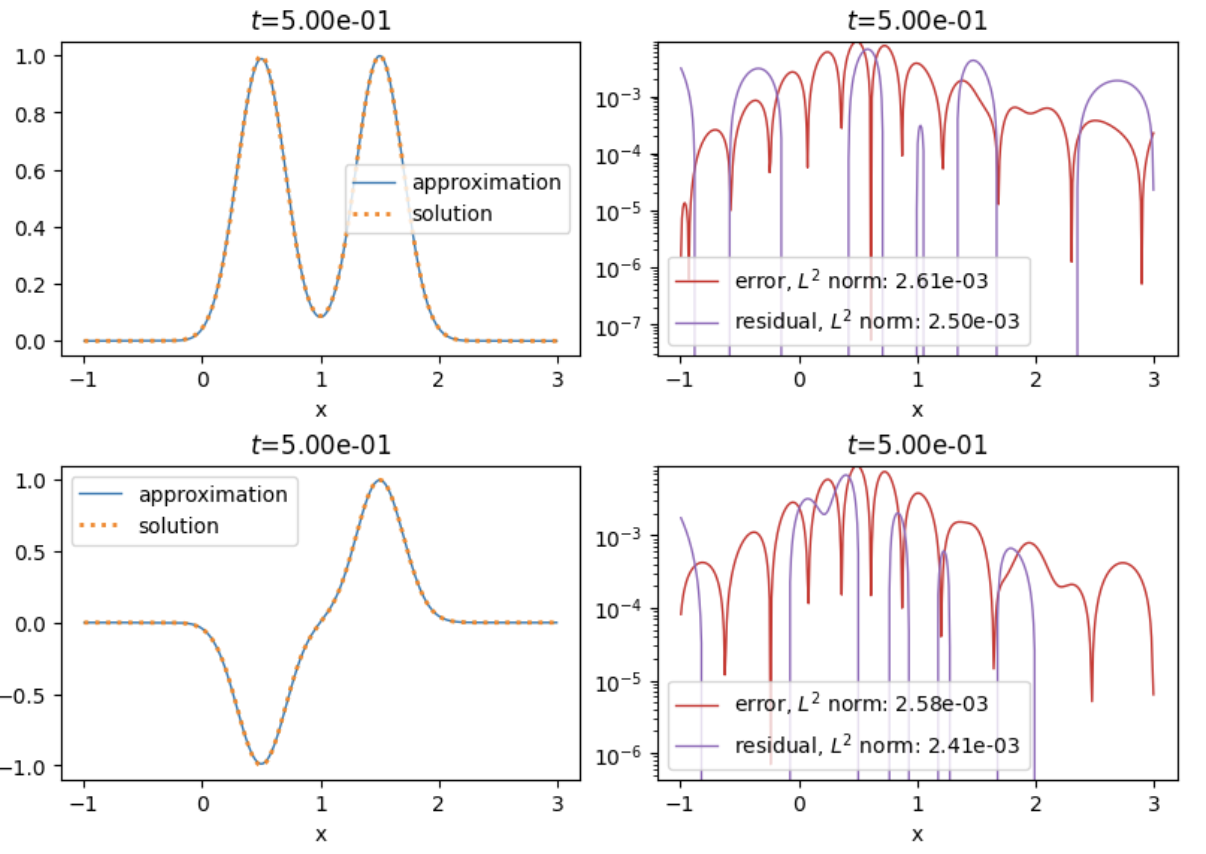
Solves the viscous Burgers advection equation in 1D using a PINN.
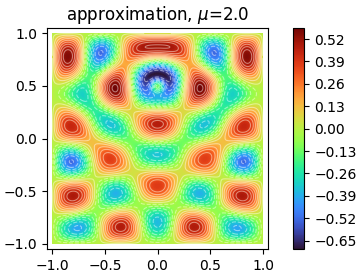
Solves an inhomogenous Helmholtz equation using a PINN and a MLP with multi-scale Fourier features.
Solves the linearized Euler system using a PINN.
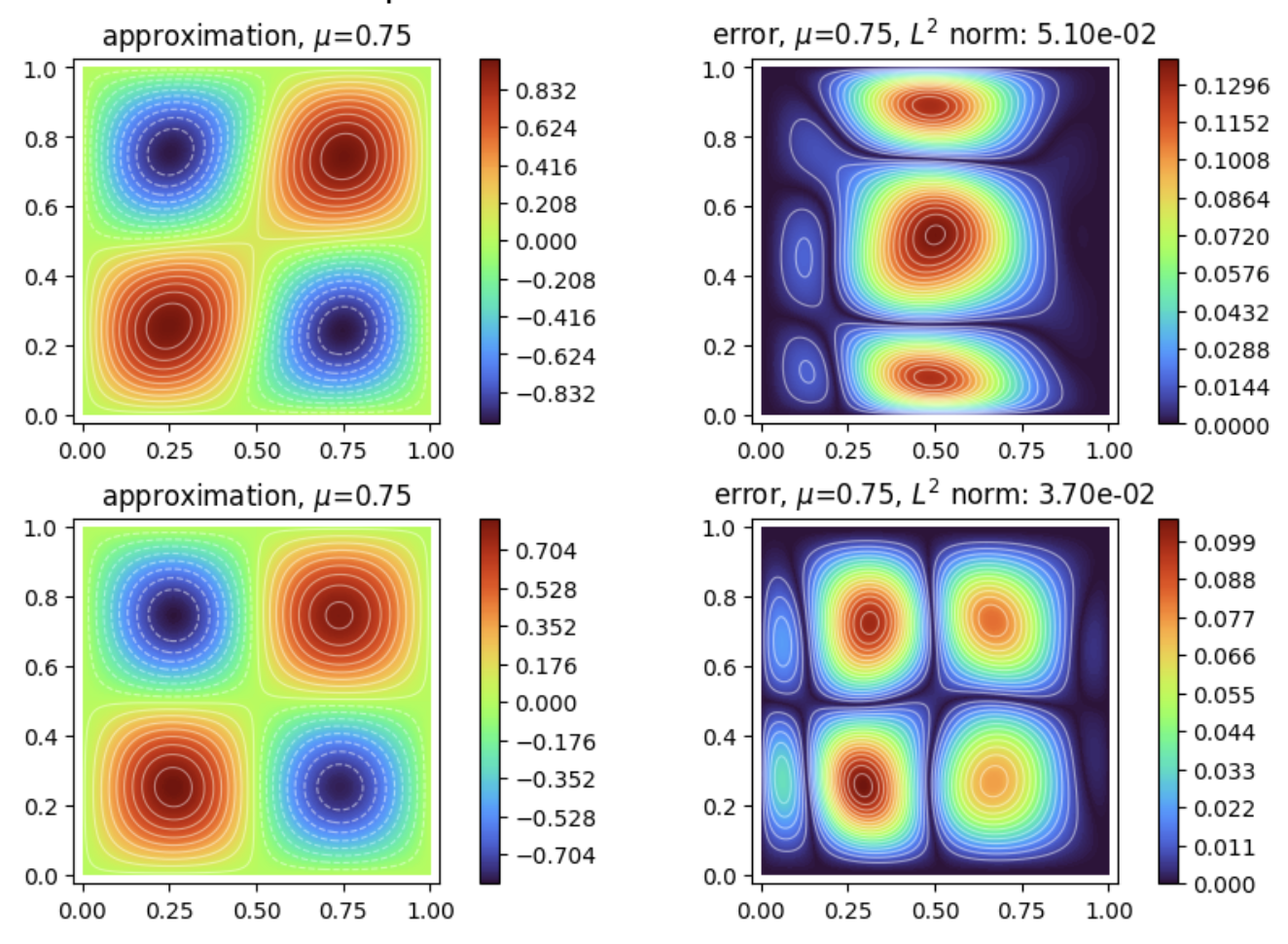
Solves a 2D grad div system with PINNs.
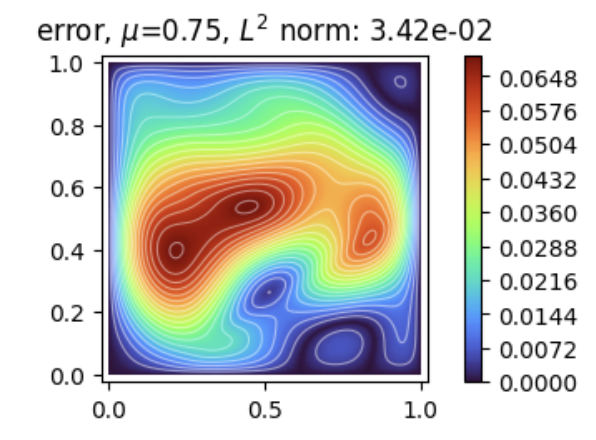
Solves a 2D div A grad u system with the deep Ritz method.
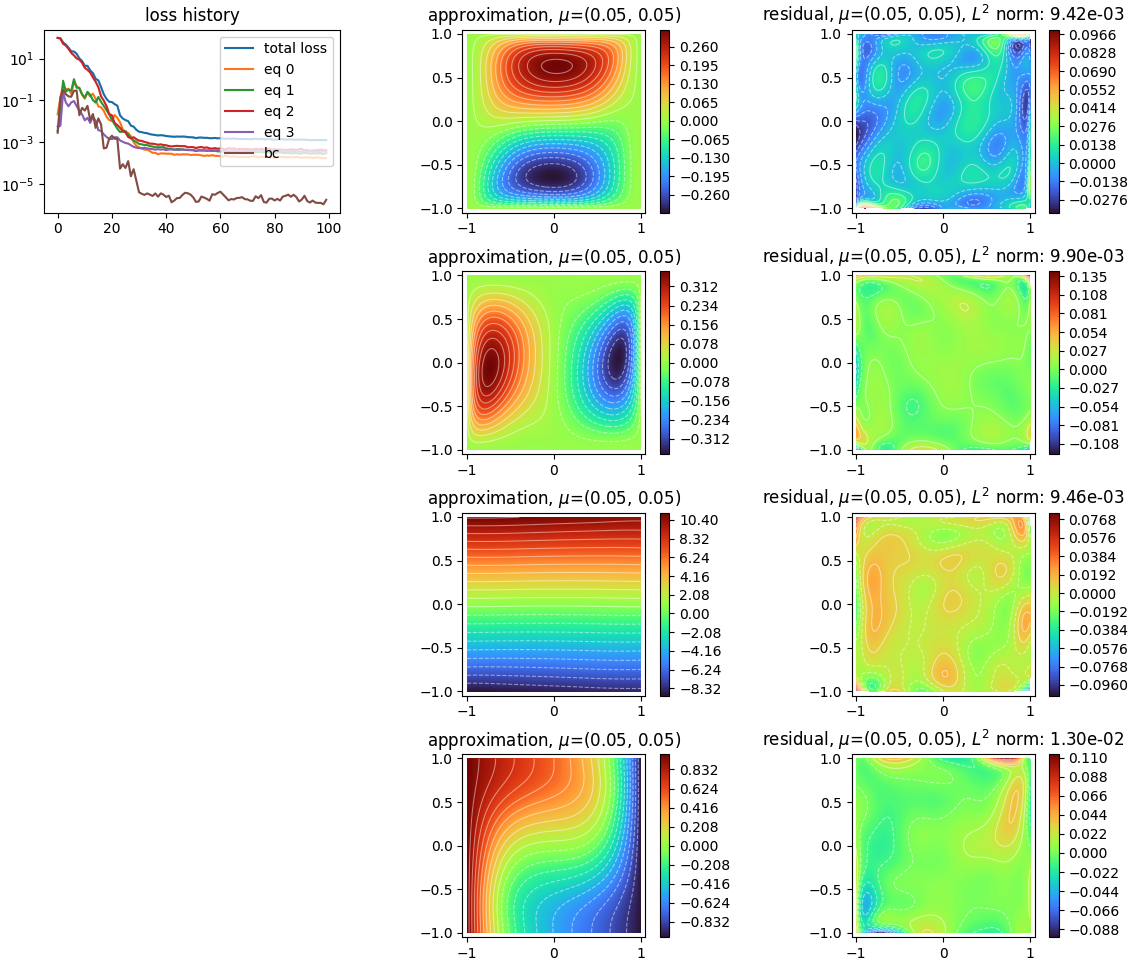
Solves a 2D Navier Stokes system with PINNs.
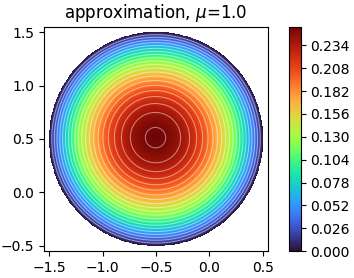
Solves a 2D laplacian on a disk with the deep Ritz method.
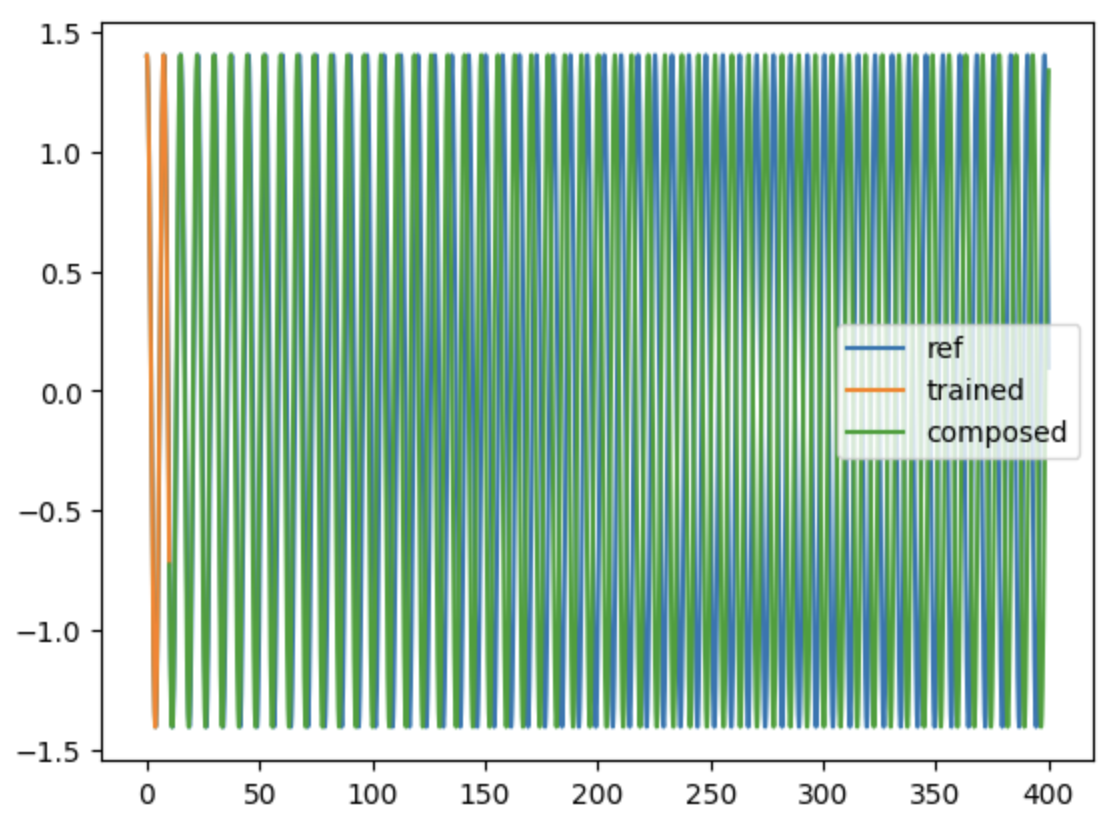
Learns the flow of a pendulum ODE with different training strategies.
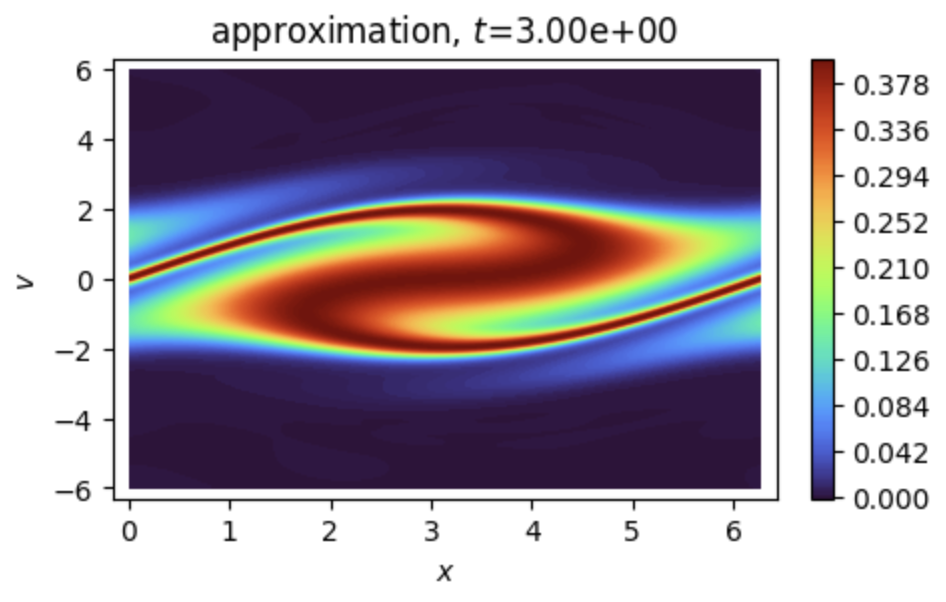
Solves a kinetic Vlasov equation in 1D with neural Semi-Lagrangian approach.
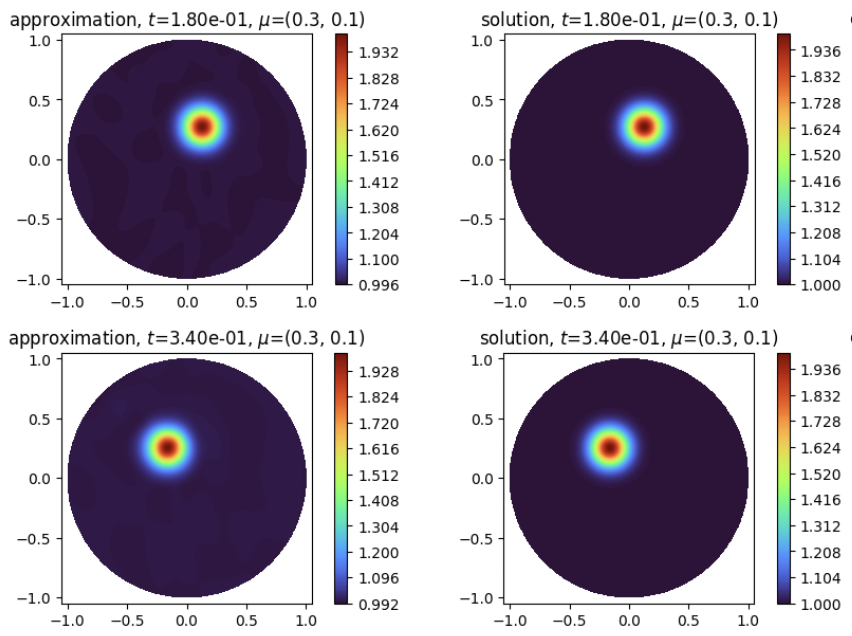
Solves a rotating transport equation in 2D with neural Galerkin approach.
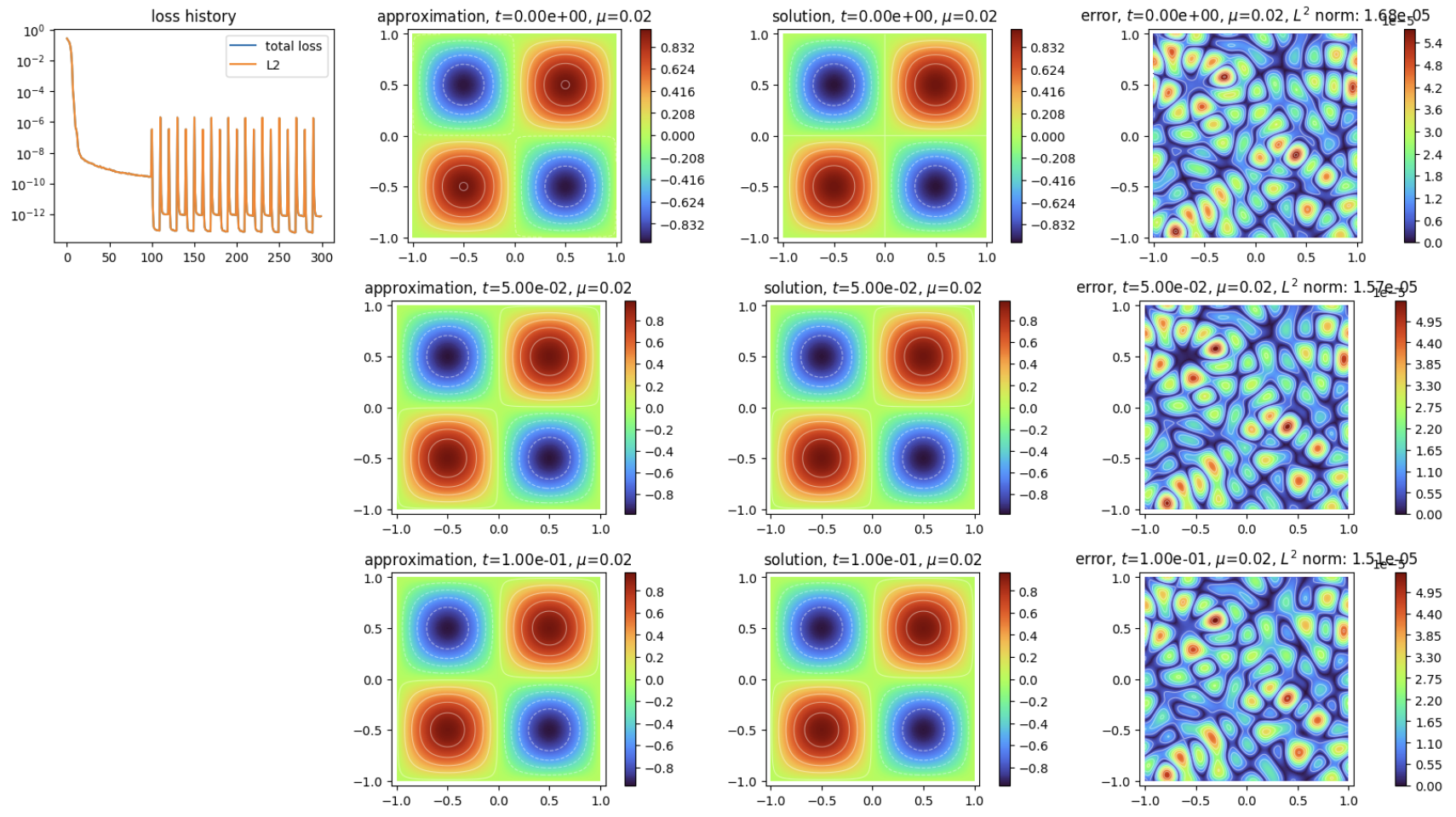
Solves a 2D heat equation with discrete pinns using implicit scheme.
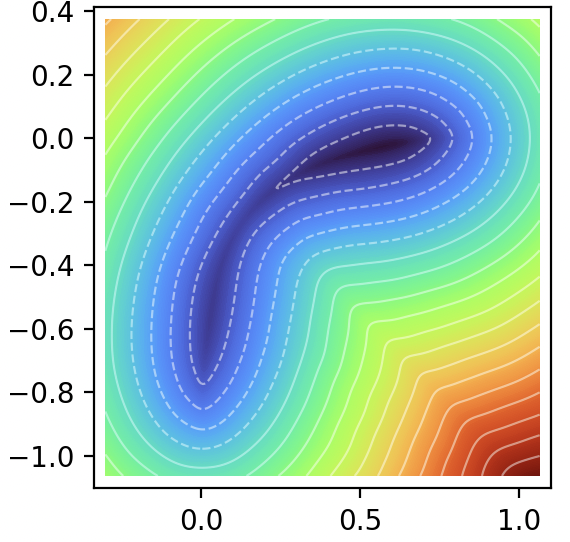
Solves a transport equation in a cylinder with neural Semi-Lagrangian approach.
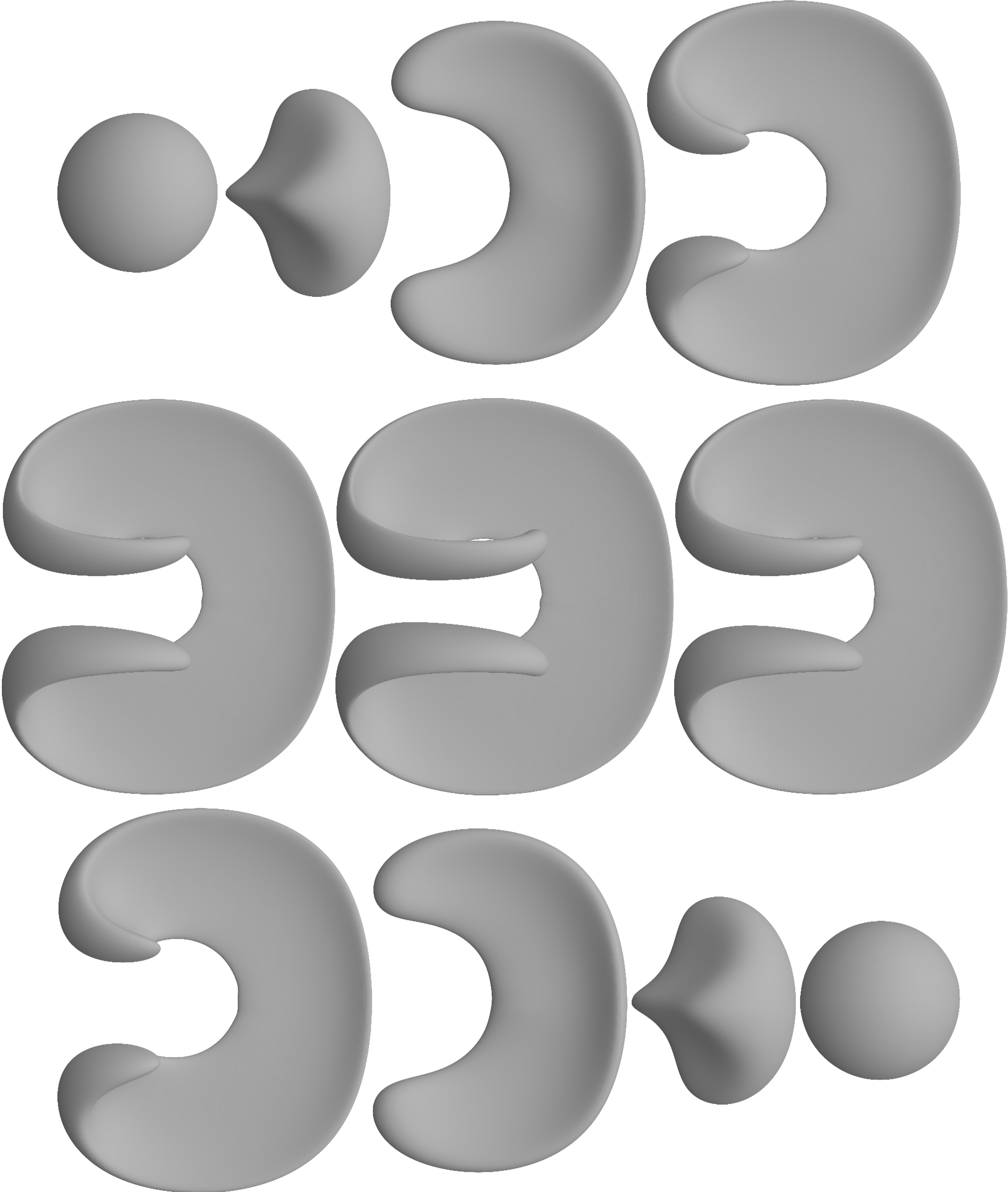
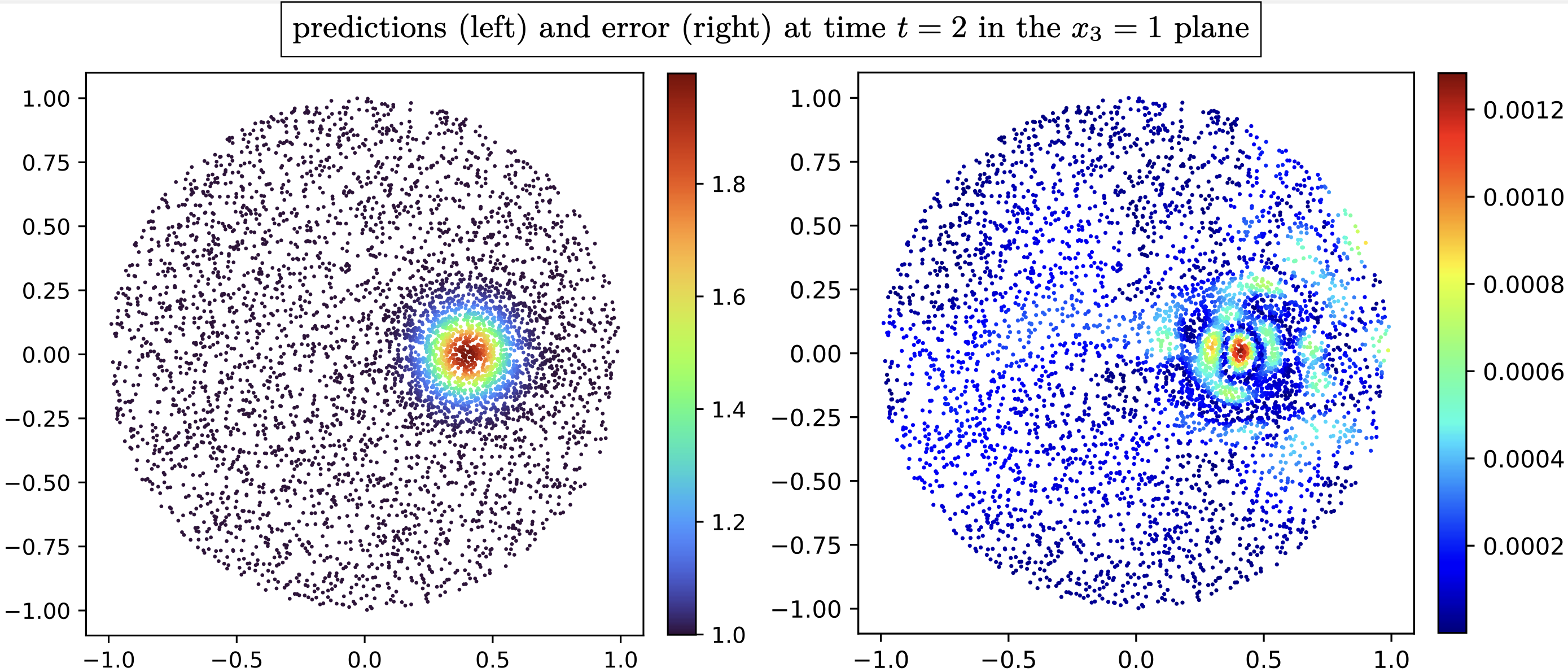
Solves the advection of a 3D level-set function with neural Semi-Lagrangian approach.
Learns the Signed Distance Function of a shape given as a file of points on its contour.
A complete list of script examples is available in the examples/
directory of the repository.
Scimba API documentation¶
Basic configuration¶
Please refer to the basic configuration page for an overview
of scimba_torch global parameters.
Available Packages¶
Defines the approximation space and its components. |
|
Defines mesh-based and meshless domains. |
|
Various numerical integrators for ODEs. |
|
Integration methods for volumetric and surfacic domains. |
|
A module implementing tools for geometry learning. |
|
Defines neural networks. |
|
Defines numerical solvers. |
|
Scimba optimizers and losses. |
|
Defines physical models. |
|
Plot utilities. |
|
Utility functions and classes. |
Development¶
Development
